What makes people accept or reject technology?
User acceptance of interactive technology was defined by Dillon (2001) as “the demonstrable willingness within a user group to employ technology for the tasks it is designed to support”. However, acceptance of autonomous systems is influenced by additional factors. A broader view on acceptance, taking into account “social aspects”, seems to become relevant for socially situated robots Fong et al (2003). In the context of HRI I define social acceptance as “an ’individuals’ willingness based on interaction experiences, to integrate a robot into an everyday social environment”. In other words, I consider social acceptance as user acceptance of technology as a social actor. In order to avoid potential misunderstandings, social acceptance in my research is not understood as the acceptance of a robot on the societal, but individual level. For the evaluation of technology acceptance, several frameworks and models already exist (an overview can be found in Venkatesh and Davis (2000)). All models are based on a three step concept: (1) the individual’s reaction on using information technology, (2) the intentions to use information technology based on the first reactions, (3) the actual usage of the technology.
Relevant Related Projects on Social Acceptance
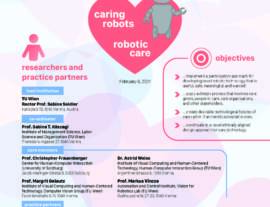
Caring Robots / Robotics Care 2022-2027
In this project, we aim to develop and implement novel and desirable roles of robotic...
Learn moreIURO 2010-2013
In this project, we developed a robot following a user-centred and human-translated...
Learn more
Relevant Related Publications on Social Acceptance
2020 |
On the Intention to Use the Pepper Robot as Communication Channel in a Business Context: Results of a User Acceptance Survey Konferenzbeitrag In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Human-Agent Interaction, S. 204–211, Association for Computing Machinery, Virtual Event, USA, 2020, ISBN: 9781450380546. |
2012 |
Studies in Public Places as a Means to Positively Influence People’s Attitude towards Robots Konferenzbeitrag In: ICSR2012: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Social Robotics, S. 209–218, Springer Berlin Heidelberg 2012. |
2011 |
The USUS evaluation framework for user-centered HRI Buchkapitel In: New Frontiers in Human–Robot Interaction, S. 89-110, John Benjamins, 2011. |
2008 |
A methodological variation for acceptance evaluation of Human-Robot Interaction in public places Konferenzbeitrag In: RO-MAN 2008 - The 17th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, S. 713-718, 2008, ISSN: 1944-9437. |